Sometimes you need your devices (say an SMTP server) to have a specific outbound public IP for things like reverse-DNS look-ups to ensure mail delivery and reputation, or maybe you want traffic from particular devices or policies to go out an IP for means of tracking.
It is not immediately obvious on Fortigates how to do this, typically, when you create a policy and NAT traffic out through it, the Fortigate will use its’ own public IP assigned by the ISP to originate the traffic from, if you have got a static IP and use an unnumbered address from your ISP then you might be lucky and your R-DNS might match this, however, in most cases you will have a separate Virtual IP for your SMTP server that is different to this and thus you need the R-DNS lookup to match that of the A-Record.
So the problem becomes:
How do I get traffic from a specific policy to originate from a static public IP of my choosing?
Fortigates have a concept called IP Pools ↗.
IP Pools are a mechanism that allow sessions leaving the FortiGate Firewall to use NAT. An IP pool defines a single IP address or a range of IP addresses to be used as the source address for the duration of the session. These assigned addresses will be used instead of the IP address assigned to that FortiGate interface.
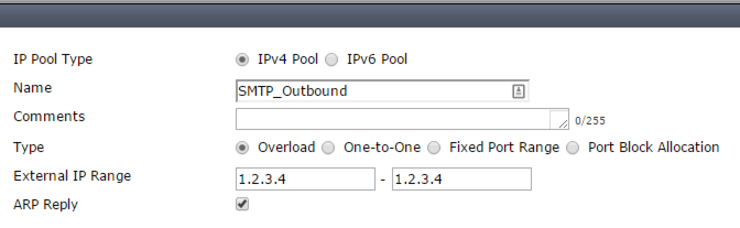
So we need to first create an IP Pool in Policy & Objects -> Objects -> IP Pools:
- Click
Create New - Set the
Name - Set the type to
Overload(To allow multiple back-end devices to use this one public IP) - Set the
External IP Rangeto be a single address in the block assigned by your ISP - Save
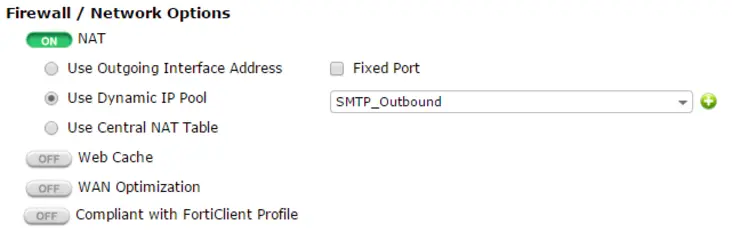
Next we need to go to Policies in the Policy & Objects -> Policy -> IPv4 section and select the policy from LAN -> WAN that contains our SMTP server and edit the Firewall/Network Options section:
- Set
NATtoON - Choose
Use Dynamic IP Pool - Specify the pool name you created before
- Save
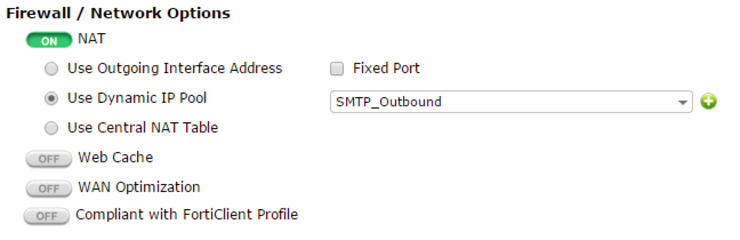
Now any traffic going to WAN through this policy will be NAT’d through the IP Pool address(es) you specified, thus, the outbound traffic from your SMTP server will originate from the same address as the R-DNS lookup for you domain’s A-Record and result in successful mail delivery.
Why not follow @mylesagray on Twitter ↗ for more like this!